版权声明:本文为GJHe原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35428201/article/details/86541523
Windows自带的ping功能可以用来测试网络的连通性,但是你真的会用吗?
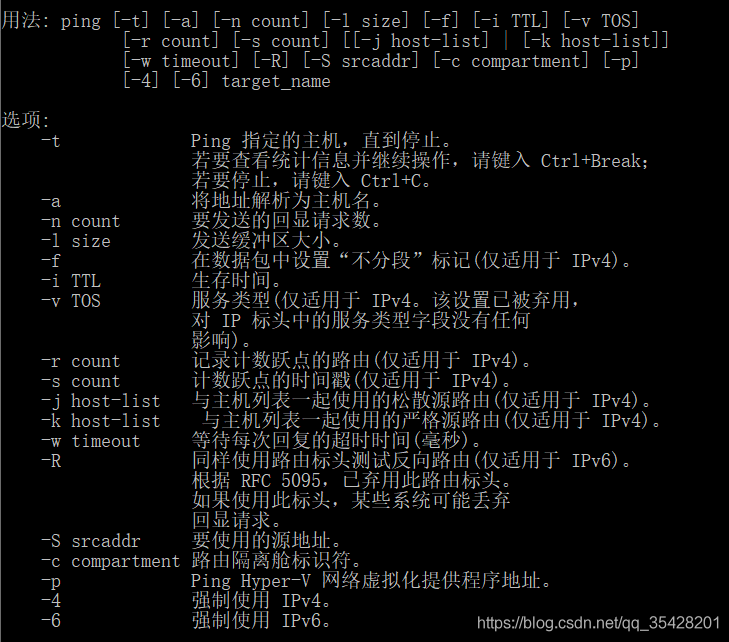
用法: ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL] [-v TOS]
[-r count] [-s count] [[-j host-list] | [-k host-list]]
[-w timeout] [-R] [-S srcaddr] [-c compartment] [-p]
[-4] [-6] target_name
选项:
-t Ping 指定的主机,直到停止。若要查看统计信息并继续操作,请键入 Ctrl+Break;若要停止,请键入 Ctrl+C。
-a 将地址解析为主机名。
-n count 要发送的回显请求数。
-l size 发送缓冲区大小。
-f 在数据包中设置“不分段”标记(仅适用于 IPv4)。
-i TTL 生存时间。
-v TOS 服务类型(仅适用于 IPv4。该设置已被弃用,对 IP 标头中的服务类型字段没有任何影响)。
-r count 记录计数跃点的路由(仅适用于 IPv4)。
-s count 计数跃点的时间戳(仅适用于 IPv4)。
-j host-list 与主机列表一起使用的松散源路由(仅适用于 IPv4)。
-k host-list 与主机列表一起使用的严格源路由(仅适用于 IPv4)。
-w timeout 等待每次回复的超时时间(毫秒)。
-R 同样使用路由标头测试反向路由(仅适用于 IPv6)。
根据 RFC 5095,已弃用此路由标头。如果使用此标头,某些系统可能丢弃回显请求。
-S srcaddr 要使用的源地址。
-c compartment 路由隔离舱标识符。
-p Ping Hyper-V 网络虚拟化提供程序地址。
-4 强制使用 IPv4。
-6 强制使用 IPv6。
Linux下的ping
PING(8) System Manager's Manual: iputils PING(8)
NAME
ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts
SYNOPSIS
ping [-aAbBdDfhLnOqrRUvV46] [-c count] [-F flowlabel] [-i interval] [-I interface] [-l preload] [-m mark] [-M pmtudisc_option] [-N nodeinfo_option] [-w deadline]
[-W timeout] [-p pattern] [-Q tos] [-s packetsize] [-S sndbuf] [-t ttl] [-T timestamp option] [hop ...] destination
DESCRIPTION
ping uses the ICMP protocol's mandatory ECHO_REQUEST datagram to elicit an ICMP ECHO_RESPONSE from a host or gateway. ECHO_REQUEST datagrams (``pings'') have an IP
and ICMP header, followed by a struct timeval and then an arbitrary number of ``pad'' bytes used to fill out the packet.
ping works with both IPv4 and IPv6. Using only one of them explicitly can be enforced by specifying -4 or -6.
ping can also send IPv6 Node Information Queries (RFC4620). Intermediate hops may not be allowed, because IPv6 source routing was deprecated (RFC5095).
OPTIONS
-4 Use IPv4 only.
-6 Use IPv6 only.
-a Audible ping.
-A Adaptive ping. Interpacket interval adapts to round-trip time, so that effectively not more than one (or more, if preload is set) unanswered probe is present
in the network. Minimal interval is 200msec for not super-user. On networks with low rtt this mode is essentially equivalent to flood mode.
-b Allow pinging a broadcast address.
-B Do not allow ping to change source address of probes. The address is bound to one selected when ping starts.
-c count
Stop after sending count ECHO_REQUEST packets. With deadline option, ping waits for count ECHO_REPLY packets, until the timeout expires.
-d Set the SO_DEBUG option on the socket being used. Essentially, this socket option is not used by Linux kernel.
-D Print timestamp (unix time + microseconds as in gettimeofday) before each line.
-f Flood ping. For every ECHO_REQUEST sent a period ``.'' is printed, while for ever ECHO_REPLY received a backspace is printed. This provides a rapid display
of how many packets are being dropped. If interval is not given, it sets interval to zero and outputs packets as fast as they come back or one hundred times
per second, whichever is more. Only the super-user may use this option with zero interval.
-F flow label
IPv6 only. Allocate and set 20 bit flow label (in hex) on echo request packets. If value is zero, kernel allocates random flow label.
-h Show help.
-i interval
Wait interval seconds between sending each packet. The default is to wait for one second between each packet normally, or not to wait in flood mode. Only
super-user may set interval to values less than 0.2 seconds.
-I interface
interface is either an address, or an interface name. If interface is an address, it sets source address to specified interface address. If interface in an
interface name, it sets source interface to specified interface. For IPv6, when doing ping to a link-local scope address, link specification (by the
'%'-notation in destination, or by this option) is required.
-l preload
If preload is specified, ping sends that many packets not waiting for reply. Only the super-user may select preload more than 3.
-L Suppress loopback of multicast packets. This flag only applies if the ping destination is a multicast address.
-m mark
use mark to tag the packets going out. This is useful for variety of reasons within the kernel such as using policy routing to select specific outbound pro‐
cessing.
-M pmtudisc_opt
Select Path MTU Discovery strategy. pmtudisc_option may be either do (prohibit fragmentation, even local one), want (do PMTU discovery, fragment locally
when packet size is large), or dont (do not set DF flag).
-N nodeinfo_option
IPv6 only. Send ICMPv6 Node Information Queries (RFC4620), instead of Echo Request. CAP_NET_RAW capability is required.
help Show help for NI support.
name Queries for Node Names.
ipv6 Queries for IPv6 Addresses. There are several IPv6 specific flags.
ipv6-global
Request IPv6 global-scope addresses.
ipv6-sitelocal
Request IPv6 site-local addresses.
ipv6-linklocal
Request IPv6 link-local addresses.
ipv6-all
Request IPv6 addresses on other interfaces.
ipv4 Queries for IPv4 Addresses. There is one IPv4 specific flag.
ipv4-all
Request IPv4 addresses on other interfaces.
subject-ipv6=ipv6addr
IPv6 subject address.
subject-ipv4=ipv4addr
IPv4 subject address.
subject-name=nodename
Subject name. If it contains more than one dot, fully-qualified domain name is assumed.
subject-fqdn=nodename
Subject name. Fully-qualified domain name is always assumed.
-n Numeric output only. No attempt will be made to lookup symbolic names for host addresses.
-O Report outstanding ICMP ECHO reply before sending next packet. This is useful together with the timestamp -D to log output to a diagnostic file and search
for missing answers.
-p pattern
You may specify up to 16 ``pad'' bytes to fill out the packet you send. This is useful for diagnosing data-dependent problems in a network. For example, -p
ff will cause the sent packet to be filled with all ones.
-q Quiet output. Nothing is displayed except the summary lines at startup time and when finished.
-Q tos Set Quality of Service -related bits in ICMP datagrams. tos can be decimal (ping only) or hex number.
In RFC2474, these fields are interpreted as 8-bit Differentiated Services (DS), consisting of: bits 0-1 (2 lowest bits) of separate data, and bits 2-7 (high‐
est 6 bits) of Differentiated Services Codepoint (DSCP). In RFC2481 and RFC3168, bits 0-1 are used for ECN.
Historically (RFC1349, obsoleted by RFC2474), these were interpreted as: bit 0 (lowest bit) for reserved (currently being redefined as congestion control),
1-4 for Type of Service and bits 5-7 (highest bits) for Precedence.
-r Bypass the normal routing tables and send directly to a host on an attached interface. If the host is not on a directly-attached network, an error is
returned. This option can be used to ping a local host through an interface that has no route through it provided the option -I is also used.
-R ping only. Record route. Includes the RECORD_ROUTE option in the ECHO_REQUEST packet and displays the route buffer on returned packets. Note that the IP
header is only large enough for nine such routes. Many hosts ignore or discard this option.
-s packetsize
Specifies the number of data bytes to be sent. The default is 56, which translates into 64 ICMP data bytes when combined with the 8 bytes of ICMP header
data.
-S sndbuf
Set socket sndbuf. If not specified, it is selected to buffer not more than one packet.
-t ttl ping only. Set the IP Time to Live.
-T timestamp option
Set special IP timestamp options. timestamp option may be either tsonly (only timestamps), tsandaddr (timestamps and addresses) or tsprespec host1 [host2
[host3 [host4]]] (timestamp prespecified hops).
-U Print full user-to-user latency (the old behaviour). Normally ping prints network round trip time, which can be different f.e. due to DNS failures.
-v Verbose output.
-V Show version and exit.
-w deadline
Specify a timeout, in seconds, before ping exits regardless of how many packets have been sent or received. In this case ping does not stop after count
packet are sent, it waits either for deadline expire or until count probes are answered or for some error notification from network.
-W timeout
Time to wait for a response, in seconds. The option affects only timeout in absence of any responses, otherwise ping waits for two RTTs.