1、API:
Java 的API(API: Application(应用) Programming(程序) Interface(接口))
简单的说就是
JDK中提供给我们使用的类,这些类将底层的代码实现封装了起来
2、Object类:
equals方法:
Object类是用来比较内存地址的:

举个例子:
创建一个人 类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class person { private String name; private int age; public person() { super(); } public person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
建立测试类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { person p1 = new person("张三",12); person p2 = new person("李四",13); System.out.println(p1); System.out.println(p2); System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)); } }
效果如下:
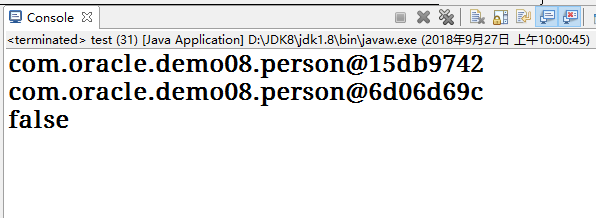
API已经将equals方法重写过了 , 直接用就可以了;
举个例子:
package com.oracle.demo08; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "abc"; String b = "abc"; System.out.println(a.equals(b)); } }
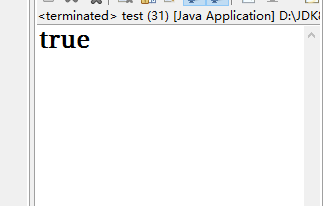
我们在实际应用中的自定义类,也可以将equals方法重写:类如比较年龄
建立人 类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class person { private String name; private int age; //重写Object类的equals方法 public boolean equals(Object obj) { //如果obj为空时 if(obj == null){ return false; } //如果obj为其自身时 if(obj == this){ return true; } //向下转型 if(obj instanceof person){ person p =(person)obj; return this.age == p.age; } return false; } public person() { super(); } public person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
建立测试类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "14"; person p1 = new person("张三",12); person p2 = new person("李四",12); person p4 = new person("李wu",14); person p3 = new person(); System.out.println(p1); System.out.println(p2); System.out.println(p3); System.out.println(p4); //空 System.out.println(p1.equals(p3));//false //自身 System.out.println(p1.equals(p1));//true //相等 System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));//true //不相等 System.out.println(p1.equals(p4));//false //类型不符 System.out.println(p1.equals(a));//false } }
toString方法:
Object类中:

toString方法返回该对象的字符串表示,其实该字符串内容就是对象的类型+@+内存地址值。
举个例子:
建立人 类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class person { private String name; private int age; public person() { super(); } public person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
建立测试类
package com.oracle.demo08; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { person p1 = new person("张三",12); person p2 = new person("李四",12); System.out.println(p1.toString()); System.out.println(p2.toString()); } }
效果如下:
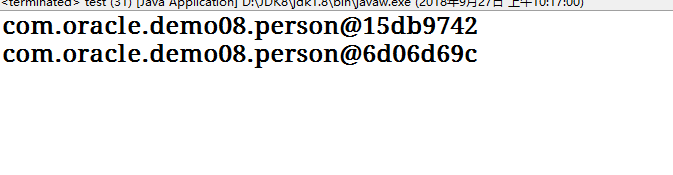
API中的toString方法已经重写了,可以进行直接使用:比如说ArrayList<T>集合类
建立一个集合:
package com.oracle.demo08; import java.util.ArrayList; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); System.out.println(list.toString()); } }
效果如下:
我们在实际应用中用到自定义类时也可以根据需求重写toString方法
举个例子:
建立人 类
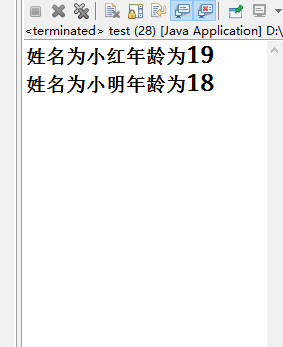
package com.oracle.demo04; public class person { private String name; private int age; //重写toString方法 public String toString() { String mes ="姓名为"+this.getName()+"年龄为"+this.getAge(); return mes; } public person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public person() { super(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
建立测试类
package com.oracle.demo04; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { person p = new person("小明",18); person p1 = new person("小红",19); System.out.println(p1); System.out.println(p); } }
效果如下: