1.概述
程序执行时的错误主要分两种,第一种是语法错误,第二种是语意错误。
通常情况下,开发工具会帮开发者诊断出语法错误,例如大家喜闻乐见的空指针异常,但语意错误开发工具却不那么容易帮开发者检测出来了,因为没有一个明确的标准,开发工具不知道到底怎样算对、怎样算错。用一位国际友人的话说就是:
- If you make an error with the syntax, you’ll have the compiler complain about it.
- If you make an error with the semantics, you’ll have people complain about it (especially your boss).
1.1 语法 & 语意
语法:在编程语言中,语法是定义符号组合的规则,它使这些符号以正确的结构或片段展示。
如:He is a man.(主、谓、宾)
语意:在编程语言理论中,语意是代码的含义,它描述了计算机用特定语言执行程序时所遵循的过程。
如:He is a man.(他是一个男人)
由上我们就可以知道,语法和语意只不过是站在不同的角度看待同一事物而已。
大致搞明白语法和语意的概念之后,大家自然就明白为什么开发工具可以轻易地帮我们检测出语法错误,但很难帮我们发现语意错误了——因为语法是死的,该什么样就什么样,不需要你来创造任何东西,只要按照规定的格式往里面填符号就好了,正如上面的例子,如果你把谓语和宾语的位置颠倒一下——He a man is,开发工具立马就可以检测出问题。但如果你将上面的句子改成——Grass eat sun,虽然这句话毫无意义,但开发工具是不知道的,因为它完全符合语法规则。因此出现语意错误时,你唯一可能惹怒的只有人——要么是你的队友,要么是你的老板。
2. 异常基本概念及继承结构
2.1 什么是异常?
异常:导致程序中断运行的一种指令流。
我们必须明确一点:即使程序异常了,它也是按照某种逻辑在执行,只是没有按照我们给它安排的逻辑执行。 但错归错,错并不代表没有逻辑,任何代码的执行一定是按照某种逻辑执行的,只是有些人能控制自己的代码,而有些人则不能。就像我们上学的时候做题一样,虽然有些题由于我们的大意在没有看清题意的情况下就直接开始做了,但在正确答案未公布之前,我们会很坚定自己的答案。尽管最终那道题我们还是得了零分,但当时解题的时候我们肯定是按照某种逻辑来写算式的,哪怕是按照错误的逻辑。这可能也是为什么有的人明明做错了事,却振振有词的原因吧。
通常情况下,我们所说的异常就是语法错误。
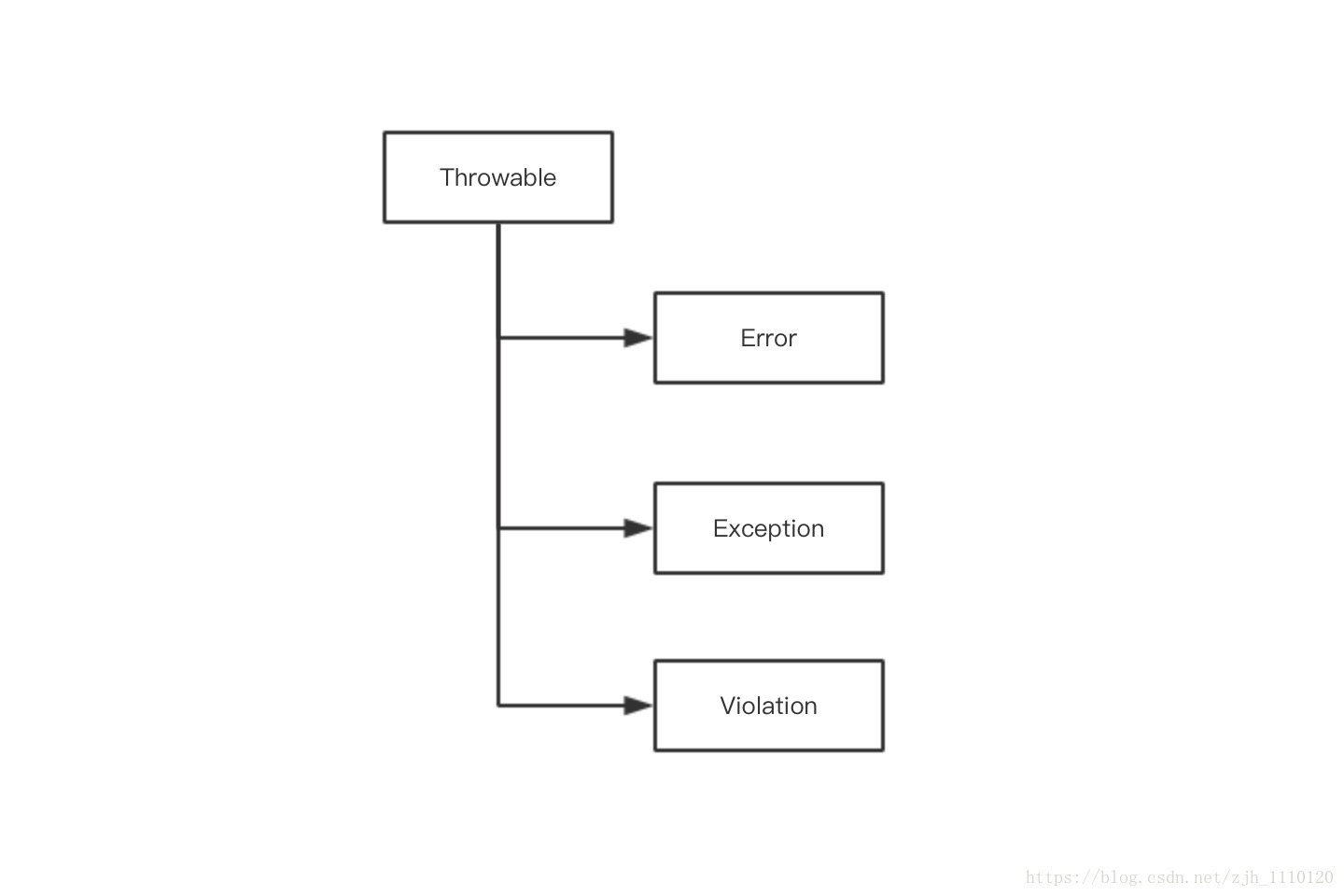
2.2 异常继承结构
考虑到 Java 中只有 Error 和 Exception,并且 Violation 在 Android 中也不常见,因此本篇文章只讲解 Error 和 Exception 。
3. 如何在程序中使用异常处理?
3.1 基础用法
try{
//有可能出现异常的语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}
...
finally{
一定会执行的代码
}例如:
//源代码
public class Test20180806 {
private static String mContent;
private static String mMSG = "天王盖地虎";
public static void main(String []args) {
try {
mContent.equals(mMSG);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
System.out.println(mMSG);
}
}
}
//执行结果
java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.smart.www.Test20180806.main(Test20180806.java:17)
天王盖地虎3.2 注意事项
1) 在 Java 中,所有捕获范围小的异常必须放在捕获范围大的异常之前,否则程序在编译时就会出现错误提示。
例如:
//源代码
public class Test20180806 {
private static String mContent;
private static String mMSG = "天王盖地虎";
public static void main(String []args) {
try {
mContent.equals(mMSG);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
System.out.println(mMSG);
}
}
}
//执行结果
此时开发工具会提醒:
Unreachable catch block for NullPointerException. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception2) 虽然 Throwable 是最大的异常类,但一般在程序中不建议直接使用 Throwable 进行异常捕获,因为 Throwable 的子类有两个——Error 和 Exception,Error 本身不需要程序处理,需要程序处理的只有 Exception,所以没必要使用 Throwable。
//源代码
//考虑到 Throwable 是 Exception 的父类,因此可以将上面的程序改成下面这个样子,虽然逻辑上没有任何问题,但这样并没有什么意义,和上面唯一的区别是:祛除了错误提示
public class Test20180806 {
private static String mContent;
private static String mMSG = "天王盖地虎";
public static void main(String []args) {
try {
mContent.equals(mMSG);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Throwable e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
System.out.println(mMSG);
}
}
}4. 如何自定义异常?
虽然 Java 中提供了大量的异常类,但有时这些异常可能很难满足我们的需求,因此我们需要根据自己的情况自定义异常类。自定义异常类的方法很简单,只需继承 Exception 即可。
如:
//源代码
public class TestException20180809 extends Exception {
public TestException20180809(){}
public TestException20180809(String message){
super(message);
}
}
public class Test20180806 {
private static String mContent;
private static String mMSG = "天王盖地虎";
public static void main(String []args) {
// try {
// mContent.equals(mMSG);
// } catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } catch (Throwable e){
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// finally{
// System.out.println(mMSG);
// }
try {
throw new TestException20180809();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
throw new TestException20180809("自定义异常:天王盖不住地虎!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//执行结果
com.smart.www.TestException20180809
at com.smart.www.Test20180806.main(Test20180806.java:28)
com.smart.www.TestException20180809: 自定义异常:天王盖不住地虎!
at com.smart.www.Test20180806.main(Test20180806.java:34)在自定义异常 TestException20180809 中,为 TestException20180809 创建了两个构造函数,通过输出结果可以看出,二者最大的不同是第二个构造函数中可以添加异常信息。但这并没有什么意义,因为在 99.9% 的情况下,我们只需要知道异常的名称就足够了。
5. Throws、Throw 用法
5.1 Throws
在定义一个方法的时候,可以用 Throws 来声明,被 Throws 声明过的方法表示此方法不处理异常。
如:
//源代码
public class Test20180809 {
public static void main(String []args){
try {
divide(10, 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void divide(int number1, int number2) throws Exception{
System.out.println(number1/number2);
}
}
//执行结果
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.smart.www.Test20180809.divide(Test20180809.java:22)
at com.smart.www.Test20180809.main(Test20180809.java:15)5.2 Throw
Throw 表示手动抛出一个异常,抛出异常的时候,直接在 Throw 后面添加异常的实例即可。
如:
//源代码
public class Test201808092037 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throw new TestException20180809("自定义异常:天王盖地虎");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//执行结果
com.smart.www.test_exception_20180806.TestException20180809: 自定义异常:天王盖地虎
at com.smart.www.test_exception_20180806.Test201808092037.main(Test201808092037.java:16)6. 异常执行流程、代码块
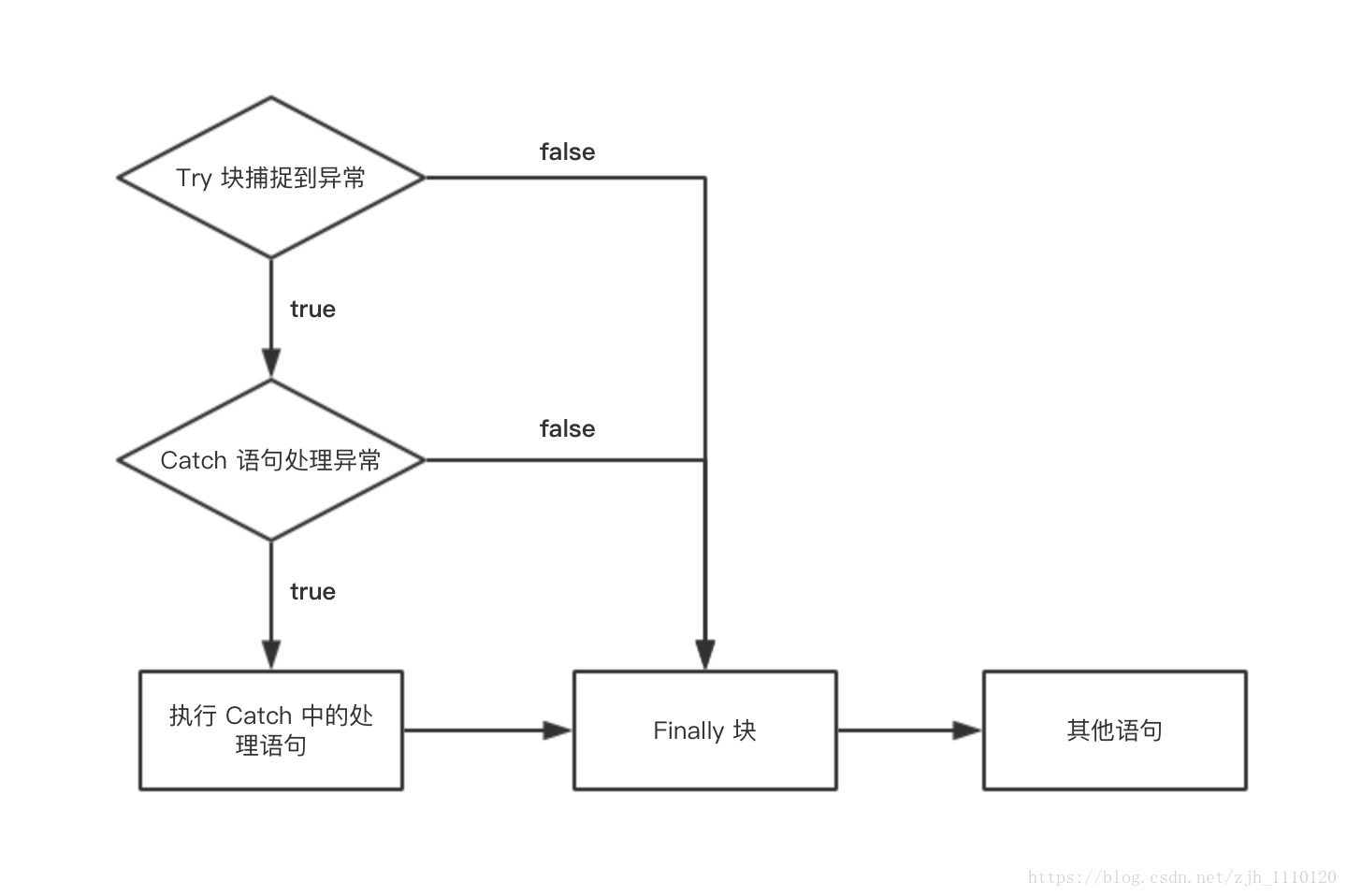
异常的执行流程正如错误的分类一样,也有两种:语法格式和语意格式。
6.1 语法格式
//语法格式
try{
//有可能出现异常的语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}catch(异常类 异常对象){
//异常处理语句
}
...
finally{
一定会执行的代码
}6.2 语意格式
正如 Try…Catch 语法格式一样,异常的执行流程图不过是用“语意”的方式将其表达出来。
7. Error 与 Exception、RuntimeException 区别
7.1 Error
Error 未检查型异常(Unchecked Exception),正常情况下不会出现,因此在定义普通方法或构造方法时不必声明。
如:
Error:java: Compilation failed: internal java compiler error从异常信息中可以看出,这明显不是我们的程序可以解决的问题,这是 Java 编译器和项目中设置的版本不一致导致的异常。
7.2 Exception
Exception 检查型异常(Checked Exception),在编译时开发工具会提示用 Try…Catch 语句捕获,即必须使用使用 Try…Catch 捕获。
如:
try {
//如果在程序中不捕获此异常,开发工具就会提示 Unhandled exception type InterruptedException
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}7.3 RuntimeException
RuntimeException 属于未检查型异常(Unchecked Exception),虽是 Exception 的子类,但在程序中不是必须使用使用 Try…Catch 捕获的,它和 Error 的区别在于,它出现在“正常”情况下。
如:
//源代码
public class Test20180806 {
private static String mContent;
private static String mMSG = "天王盖地虎";
public static void main(String []args) {
try {
mContent.equals(mMSG);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Throwable e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
System.out.println(mMSG);
}
}
}
//执行结果
java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.smart.www.Test20180806.main(Test20180806.java:17)
天王盖地虎8. 当异常捕获遇上 Return
8.1 场景分析
异常捕获和 Return 联合使用的情况,可以分为如下八种:
| 序号 | 具体场景 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return |
| 2 | Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体无 Return(与 Catch 冲突) |
| 3 | Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return(与 Finally 冲突) |
| 4 | Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return(与 Finally 冲突) |
| 5 | Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return |
| 6 | Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return |
| 7 | Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return(与 Finally 冲突) |
| 8 | Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return(与 Finally 冲突) |
8.2 详细分析
1) Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Try Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Method…
Method Feedback结论:当 “Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Method 体,并且由 Try 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块和 Method 体,并且由 Method 体提供返回值。
2) Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体无 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Try Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
//此处的代码开发工具会提示:Unreachable code,故作删除处理
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Catch Return结论:当 “Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体无 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Catch 语句,并且由 Try 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Catch 语句提供返回值。
3) Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Finally Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Finally Return结论:当 “Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Catch 语句,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值。
4) Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Finally Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
return "Try Return";
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Finally Return结论:当 “Try 块中有 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Catch 语句,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值。
5) Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Method…
Method Feedback
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Method…
Method Feedback结论:当 “Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块和 Method 体,不走 Catch 语句,并且由 Method 体提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块和 Method 体,并且由 Method 体提供返回值。
6) Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Method…
Method Feedback
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
}
System.out.println("Method…");
return "Method Feedback";
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Catch Return结论:当 “Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中无 Return,方法体有 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块和 Method 体,不走 Catch 语句,并且由 Method 体提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Catch 语句提供返回值。
7) Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Finally Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Finally Return结论:当 “Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中无 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Catch 语句、 Method 体,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值。
8) Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return
//源代码 无异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Finally…
Finally Return
//源代码 有异常
public class Test201808092310 {
private static String mContent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(returnTest());
}
private static String returnTest(){
try {
System.out.println("Try…");
System.out.println(mContent.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Catch…");
return "Catch Return";
}
finally {
System.out.println("Finally…");
return "Finally Return";
}
}
}
//执行结果
Try…
Catch…
Finally…
Finally Return结论:当 “Try 块中无 Return,Catch 语句中有 Return,Finally 块中有 Return,方法体无 Return” 时,无异常出现时,只走 Try 块、Finally 块,不走 Catch 语句、 Method 体,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值;有异常出现时,走 Try 块、Catch 语句、Finally 块,并且由 Finally 块提供返回值。
综合以上八条,可以得出一个结论:在一个方法中,无论 Try 块中有没有异常、Return,只要 Finally 块中有 Return,那么函数的返回值都由 Finally 块提供。
参考文档
1)《Java 开发实战经典》
2)《Thinking in Java》
3)《Android Developer Document》