- 1、第一个程序如下:
(1)首先在桌面建立一个python文件,注意Python文件最好以.py命名。
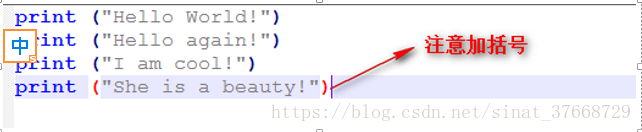
(2)建立test.py文件,内容如下:
- ”#“作用是:对一行进行注释操作!
- 怎么在代码中输入我们国家的语言文字: 在文件开头加入一行 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
(3)运行程序。进入建立的test.py文件夹,然后在powershell 运行如下代码:python test.py
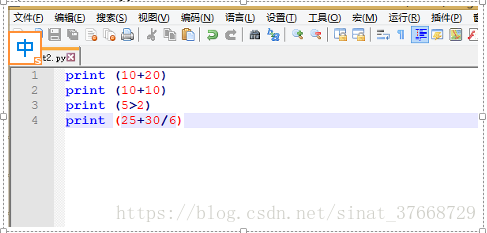
- 2、数字和数学计算
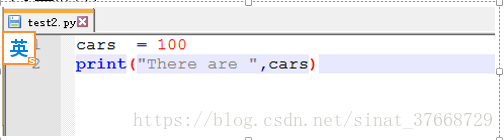
- 3、变量和命名
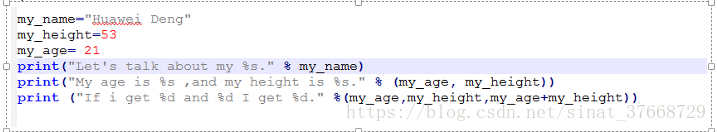
- 4、更多的变量和打印
- %r 是非常有用的,不管什么都打印出来。
- round()函数,将浮点数四舍五入
- print ("." * 10) 意思是输出10个‘.’
- 使用%r是\n换行就不灵了。
- 使用如下方式按原格式打印出:
print ("""
I am a chinese.
I am very Happy!
I want to go home.

I hope someone else will accompany me.
""")
- 转义序列:
转义字符 功能
\\ 反斜杠(\)
\' 单引号(')
\" 双引号(")
\a ASCII 响铃符
\r ASCII 回车符
\t ASCII 水平制表符
\n ASCII 换行符
…
- 记住一条:%r用于调试,%s用于显示
- 在windows终端查看测试:
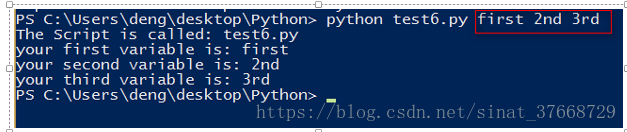
- 注意,在使用from sys import argv时,要手动输入一些值,以使得相互匹配:
源代码:
from sys import argv
script,first,second,third = argv
print ("The Script is called:",script)
print ("your first variable is:",first)
print ("your second variable is:",second)
print ("your third variable is:",third)
运行时:
- 读取文件里的内容:
from sys import argv
script ,filename = argv
txt = open(filename)
print ("Here's your file %r:" %filename)
print (txt.read())
print ("Type the filename again:")
file_again = input("> ")
txt_again = open (file_again)
print (txt_again.read())
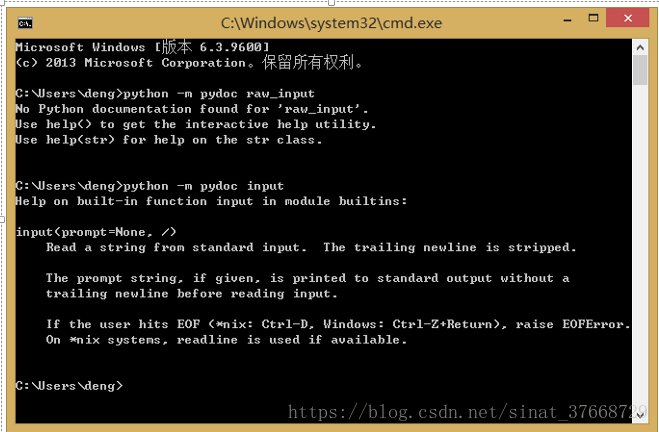
- 如何看一个命令的说明:
python -m pydoc name 即可。 - 笔记命令:
(1)close—— 关闭文件,跟你的编辑器的“文件”->“保存“是一个意思
(2)read——读取文件内容,你可以把结果赋给一个变量
(3)readline——读取文本文件中的一行
(4)truncate——清空文件,请小心使用该命令
(5)write(stuff)——将stuff写入文件
- 读写文件代码:
from sys import argv
script,filename = argv
print ("We're going to erase %r." % filename)
print ("If you don't want that ,hit CTRL-c(^c).")
print ("If you want to do that,hit RETURN")
input("?")
print ("Opening the file...")
target = open (filename,'w')
print ("Truncating the file. Goodbye!")
target.truncate();
print ("Now I'm going to ask you for three lines.")
line1 = input ("line1:")
line2 = input ("line2:")
line3 = input ("line3:")
print ("I'm going to write these to the file.")
target.write(line1)
target.write("\n")
target.write(line2)
target.write("\n")
target.write(line3)
target.write("\n")
print ("And finally,we close it.")
target.close()
- 如果你用 'w' 模式打开文件,那么你是不是还要 target.truncate() 呢?阅读以下 Python 的 open 函数的文档找找答案。
target.truncate() 是清空的意思,与“w”模式并不冲突,也并非后置条件。
- 将一个文件的内容复制到另外一个文件中去:
from sys import argv
from os.path import exists
script , from_file ,to_file = argv
print ("Copying from %s to %s" % (from_file,to_file))
#we could do these two on one file too,how ?
in_file = open(from_file)
indata = in_file.read()
print ("The input file is %d bytes long " % len(indata))
print ("Dose the output file exist? %r" % exists(to_file))
print ("Ready,hit RETURN to cotinue,CTRL+C to abort.")
input()
out_file = open(to_file,"w")
out_file.write(indata)
print ("Alright, all done.")
out_file.close()
in_file.close()
- 如何通过import来调用exists命令?
这个命令将文件名字符串作为参数,如果文件存在的话,它将返回True;否则返回False.
import调用:from os.path import exists
- Len()函数,会以数的形式返回你传递的字符串的长度。