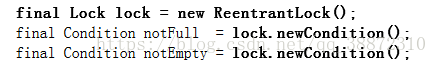Condition 将 Object 监视器方法(wait、notify 和 notifyAll)分解成截然不同的对象,以便通过将这些对象与任意 Lock 实现组合使用,为每个对象提供多个等待 set(wait-set)。其中,Lock 替代了 synchronized 方法和语句的使用,Condition 替代了 Object 监视器方法的使用。
Condition 实例实质上被绑定到一个锁上。要为特定 Lock 实例获得 Condition 实例,请使用其 newCondition() 方法。Condition 实现可以提供不同于 Object 监视器方法的行为和语义,比如受保证的通知排序,或者在执行通知时不需要保持一个锁。
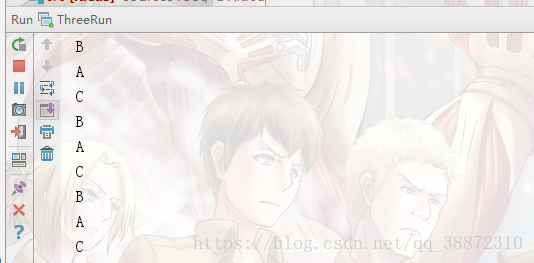
情景一:三个线程,线程1打印A,线程2打印B,线程3打印C
public class ThreeRun {
public void printB() {
System.out.println("B");
}
public void printA() {
System.out.println("A");
}
public void printC() {
System.out.println("C");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreeRun threeRun = new ThreeRun();
A a = new A(threeRun);
B b = new B(threeRun);
C c = new C(threeRun);
new Thread(a).start();
new Thread(b).start();
new Thread(c).start();
}
static class A implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun threeRun;
public A(ThreeRun threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printA();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class B implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun threeRun;
public B(ThreeRun threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printB();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class C implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun threeRun;
public C(ThreeRun threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printC();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}场景二、三个线程,线程1打印A,线程2打印B,线程3打印C (保证顺序打印,ABCABC....)
public class ThreeRun2 {
//用作判断的信号 0执行A,1执行B,2执行C
private int single=0;
public synchronized void printB() {
while (single!=1){
try {
//本线程等待 释放锁
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("B");
//增量,保证顺序性
single++;
//通知其他的线程
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void printA() {
while (single!=0){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("A");
single++;
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void printC() {
while (single!=2){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("C");
//为保证紧接着打印A,将增量清零
single=0;
notifyAll();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreeRun2 threeRun = new ThreeRun2();
A a = new A(threeRun);
B b = new B(threeRun);
C c = new C(threeRun);
new Thread(a).start();
new Thread(b).start();
new Thread(c).start();
}
static class A implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun2 threeRun;
public A(ThreeRun2 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printA();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class B implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun2 threeRun;
public B(ThreeRun2 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printB();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class C implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun2 threeRun;
public C(ThreeRun2 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printC();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
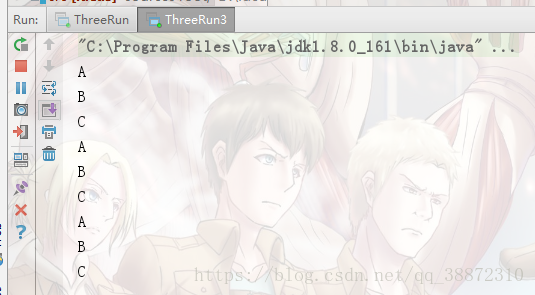
}场景三、三个线程,线程1打印A,线程2打印B,线程3打印C (保证顺序打印,ABCABC.... 换用condition的方式实现)
public class ThreeRun3 {
private int single=0;
//Condition是一个接口,在ReentrantLock里有实现
Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
//分别获取三个条件锁
Condition a=lock.newCondition();
Condition b=lock.newCondition();
Condition c=lock.newCondition();
public void printB() {
lock.lock();
while (single!=1){
try {
//相当于Object的wait()
b.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("B");
single++;
//相当于nodifyAll()
c.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
public void printA() {
lock.lock();
while (single!=0){
try {
a.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("A");
single++;
b.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
public void printC() {
lock.lock();
while (single!=2){
try {
c.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("C");
single=0;
a.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreeRun3 threeRun = new ThreeRun3();
A a = new A(threeRun);
B b = new B(threeRun);
C c = new C(threeRun);
new Thread(a).start();
new Thread(b).start();
new Thread(c).start();
}
static class A implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun3 threeRun;
public A(ThreeRun3 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printA();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class B implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun3 threeRun;
public B(ThreeRun3 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printB();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class C implements Runnable {
private ThreeRun3 threeRun;
public C(ThreeRun3 threeRun) {
this.threeRun = threeRun;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
threeRun.printC();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}使用说明:这个是API中给出的实例说明
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
2366324 查看本文章


condition要和Lock锁的实现类一起使用。
unlock()要与finally代码块一起使用。
await()要与Object的wait()区分开。