非原创,做一个知识点的传播者~~
因为fabric里面读取配置文件等使用的是viper,这里也学习一下,做个使用笔记。
go get github.com/spf13/viper
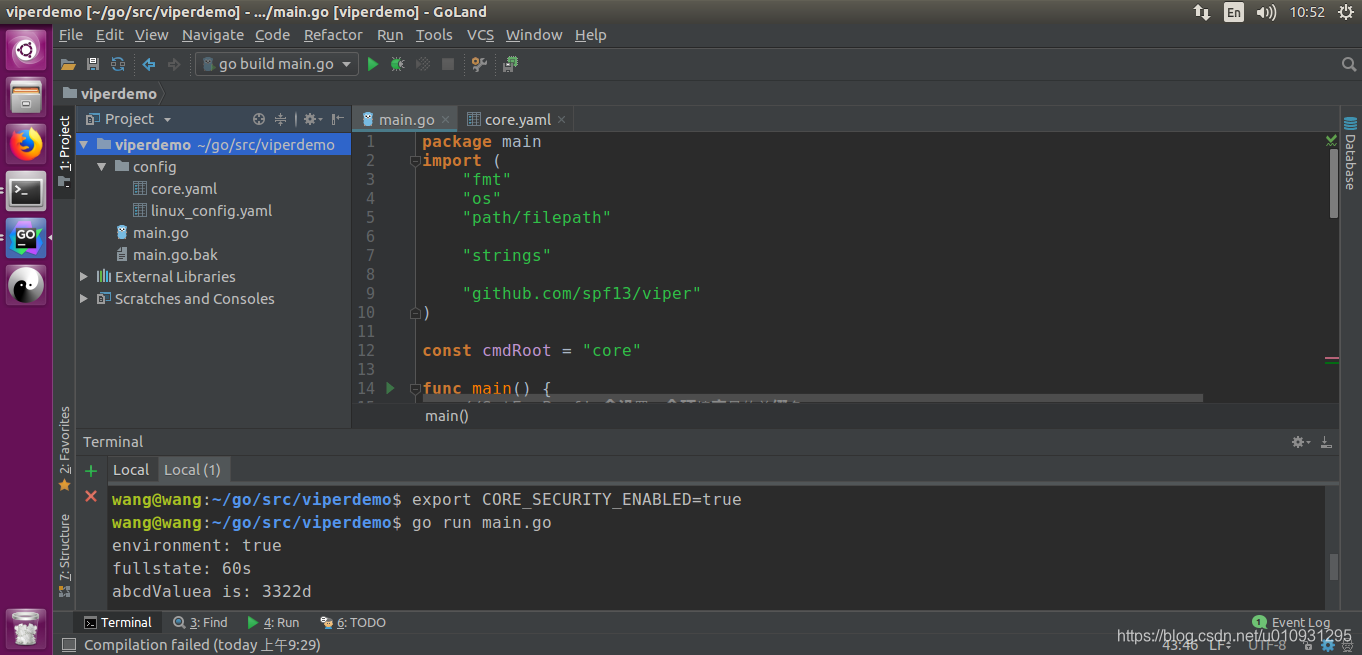
其中main.go内容:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"path/filepath"
"strings"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
const cmdRoot = "core"
func main() {
//SetEnvPrefix会设置一个环境变量的前缀名
viper.SetEnvPrefix(cmdRoot)
//会获取所有的环境变量,同时如果设置过了前缀则会自动补全前缀名
viper.AutomaticEnv()
replacer := strings.NewReplacer(".", "_")
viper.SetEnvKeyReplacer(replacer)
viper.SetConfigName(cmdRoot)
viper.AddConfigPath("./config")
viper.SetConfigType("yaml")
gopath := os.Getenv("GOPATH")
for _, p := range filepath.SplitList(gopath) {
peerpath := filepath.Join(p, "src/viperdemo")
viper.AddConfigPath(peerpath)
}
//在./config以及$GOPATH/src/viperdemo下寻找名为cmdRoot即“core”、类型为yaml的文件,core.yaml,读取里面的配置
err := viper.ReadInConfig() // Find and read the config file
if err != nil { // Handle errors reading the config file
fmt.Println(fmt.Errorf("Fatal error when reading %s config file: %s\n", cmdRoot, err))
}
//security.enabled的.替换成_,同时前面加上前缀core,环境变量前缀大小写不区分
//export CORE_SECURITY_ENABLED=TRUE
environment := viper.GetBool("security.enabled")
fmt.Println("environment:", environment)
fullstate := viper.GetString("statetransfer.timeout.fullstate")
fmt.Println("fullstate:", fullstate)
abcdValuea := viper.GetString("peer.abcd")
fmt.Println("abcdValuea is:", abcdValuea)
}
core.yaml内容:
statetransfer:
# Should a replica attempt to fix damaged blocks?
# In general, this should be set to true, setting to false will cause
# the replica to panic, and require a human's intervention to intervene
# and fix the corruption
recoverdamage: true
# The number of blocks to retrieve per sync request
blocksperrequest: 20
# The maximum number of state deltas to attempt to retrieve
# If more than this number of deltas is required to play the state up to date
# then instead the state will be flagged as invalid, and a full copy of the state
# will be retrieved instead
maxdeltas: 200
# Timeouts
timeout:
# How long may returning a single block take
singleblock: 2s
# How long may returning a single state delta take
singlestatedelta: 2s
# How long may transferring the complete state take
fullstate: 60s
peer:
abcd: 3322d
更多用法:http://www.cnblogs.com/cnblogs-wangzhipeng/p/9484460.html
本文主要是为读者介绍一个轻便好用的Golang配置库viper
正文
viper 的功能
viper 支持以下功能:
1. 支持Yaml、Json、 TOML、HCL 等格式的配置
2. 可以从文件、io、环境变量、command line中提取配置
3. 支持自动转换的类型解析
4. 可以远程从etcd中读取配置
示例代码
定义一个类型:
type config struct {
v *viper.Viper;
}
用于测试的Yaml配置文件 config.yaml
TimeStamp: "2018-07-16 10:23:19"
Author: "WZP"
PassWd: "Hello"
Information:
Name: "Harry"
Age: "37"
Alise:
- "Lion"
- "NK"
- "KaQS"
Image: "/path/header.rpg"
Public: false
Favorite:
Sport:
- "swimming"
- "football"
Music:
- "zui xuan min zu feng"
LuckyNumber: 99
读取yaml配置文件:
func LoadConfigFromYaml (c *config) error {
c.v = viper.New();
//设置配置文件的名字
c.v.SetConfigName("config")
//添加配置文件所在的路径,注意在Linux环境下%GOPATH要替换为$GOPATH
c.v.AddConfigPath("%GOPATH/src/")
c.v.AddConfigPath("./")
//设置配置文件类型
c.v.SetConfigType("yaml");
if err := c.v.ReadInConfig(); err != nil{
return err;
}
log.Printf("age: %s, name: %s \n", c.v.Get("information.age"), c.v.Get("information.name"));
return nil;
}
注意:如果不用AddConfigPath去指定路径,它会在程序执行的目录去寻找config.yaml
从IO中读取配置:
//由IO读取配置
func ReadConfigFormIo(c *config) error {
c.v = viper.New()
if f, err := os.Open("config.yaml"); err != nil{
log.Printf("filure: %s", err.Error());
return err;
}else {
confLength, _ :=f.Seek(0,2);
//注意,通常写c++的习惯害怕读取字符串的时候越界,都会多留出一个NULL在末尾,但是在这里不行,会报出如下错误:
//While parsing config: yaml: control characters are not allowed
//错误参考网址:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33717799/go-yaml-control-characters-are-not-allowed-error
configData := make([]byte, confLength);
f.Seek(0, 0);
f.Read(configData);
log.Printf("%s\n", string(configData))
c.v.SetConfigType("yaml");
if err := c.v.ReadConfig(bytes.NewBuffer(configData)); err != nil{
log.Fatalf(err.Error());
}
}
log.Printf("age: %s, name: %s \n", c.v.Get("information.age"), c.v.Get("information.name"));
return nil;
}
上面的代码是把配置文件中的数据导入IO,然后再从IO中读取
从环境变量中读取配置
//读取本地的环境变量
func EnvConfigPrefix(c *config) error {
c.v = viper.New();
//BindEnv($1,$2)
// 如果只传入一个参数,则会提取指定的环境变量$1,如果设置了前缀,则会自动补全 前缀_$1
//如果传入两个参数则不会补全前缀,直接获取第二参数中传入的环境变量$2
os.Setenv("LOG_LEVEL", "INFO");
if nil == c.v.Get("LOG_LEVEL ") {
log.Printf("LOG_LEVEL is nil");
}else {
return ErrorNotMacth;
}
//必须要绑定后才能获取
c.v.BindEnv("LOG_LEVEL");
log.Printf("LOG_LEVEL is %s", os.Getenv("log_level"));
//会获取所有的环境变量,同时如果过设置了前缀则会自动补全前缀名
c.v.AutomaticEnv();
//环境变量前缀大小写不区分
os.Setenv("DEV_ADDONES","none");
log.Printf("DEV_ADDONES: %s", c.v.Get("dev_addones"));
//SetEnvPrefix会设置一个环境变量的前缀名
c.v.SetEnvPrefix("DEV");
os.Setenv("DEV_MODE", "true");
//此时会自动补全前缀,实际去获取的是DEV_DEV_MODE
if nil == c.v.Get("dev_mode"){
log.Printf("DEV_MODE is nil") ;
}else {
return ErrorNotMacth;
}
//此时我们直接指定了loglevel所对应的环境变量,则不会去补全前缀
c.v.BindEnv("loglevel", "LOG_LEVEL");
log.Printf("LOG_LEVEL: %s", c.v.Get("loglevel")) ;
return nil
}
SetEnvPrefix 和 AutomaticEnv、BindEnv搭配使用很方便,比如说我们把当前程序的环境变量都设置为xx_ ,这样方便我们管理,也避免和其他环境变量冲突,而在读取的时候又很方便的就可以读取。
方便的替换符
func EnvCongiReplacer(c *config, setPerfix bool) error {
c.v = viper.New();
c.v.AutomaticEnv();
c.v.SetEnvKeyReplacer(strings.NewReplacer(".","_"));
os.Setenv("API_VERSION","v0.1.0");
//Replacer和prefix一起使用可能会冲突,比如我下面的例子
//因为会自动补全前缀最终由获取API_VERSION变成API_API_VERSION
if setPerfix{ c.v.SetEnvPrefix("api");}
if s := c.v.Get("api.version"); s==nil{
return ErrorNoxExistKey
}else {
log.Printf("%s", c.v.Get("api.version"));
}
return nil;
}
我们有时候需要去替换key中的某些字符,来转化为对应的环境变脸,比如说例子中将’ . ‘替换为’_’ ,由获取api.version变成了api_version,但是有一点需要注意的,SetEnvPrefix和SetEnvKeyReplacer一起用的时候可能会混淆。
别名功能
//设置重载 和别名
func SetAndAliases(c *config) error {
c.v = viper.New();
c.v.Set("Name","wzp");
c.v.RegisterAlias("id","Name");
c.v.Set("id","Mr.Wang");
//我们可以发现当别名对应的值修改之后,原本的key也发生变化
log.Printf("id %s, name %s",c.v.Get("id"),c.v.Get("name") );
return nil;
}
我们可以为key设置别名,当别名的值被重置后,原key对应的值也会发生变化。
序列化和反序列化
type favorite struct {
Sports []string;
Music []string;
LuckyNumber int;
}
type information struct {
Name string;
Age int;
Alise []string;
Image string;
Public bool
}
type YamlConfig struct {
TimeStamp string
Author string
PassWd string
Information information
Favorite favorite;
}
//将配置解析为Struct对象
func UmshalStruct(c *config) error {
LoadConfigFromYaml(c);
var cf YamlConfig
if err := c.v.Unmarshal(&cf); err != nil{
return err;
}
return nil;
}
func YamlStringSettings(c *config) string {
c.v = viper.New();
c.v.Set("name", "wzp");
c.v.Set("age", 18);
c.v.Set("aliase",[]string{"one","two","three"})
cf := c.v.AllSettings()
bs, err := yaml.Marshal(cf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to marshal config to YAML: %v", err)
}
return string(bs)
}
func JsonStringSettings(c *config) string {
c.v = viper.New();
c.v.Set("name", "wzp");
c.v.Set("age", 18);
c.v.Set("aliase",[]string{"one","two","three"})
cf := c.v.AllSettings()
bs, err := json.Marshal(cf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to marshal config to YAML: %v", err)
}
return string(bs)
}
超级实惠的一个功能,直接把配置反序列化到一个结构体,爽歪歪有木有?也可以把设置直接序列化为我们想要的类型:yaml、json等等
从command Line中读取配置
func main() {
flag.String("mode","RUN","please input the mode: RUN or DEBUG");
pflag.Int("port",1080,"please input the listen port");
pflag.String("ip","127.0.0.1","please input the bind ip");
//获取标准包的flag
pflag.CommandLine.AddGoFlagSet(flag.CommandLine);
pflag.Parse();
//BindFlag
//在pflag.Init key后面使用
viper.BindPFlag("port", pflag.Lookup("port"));
log.Printf("set port: %d", viper.GetInt("port"));
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine);
log.Printf("set ip: %s", viper.GetString("ip"));
}
可以使用标准的flag也可以使用viper包中自带的pflag,作者建议使用pflag。
监听配置文件
//监听配置文件的修改和变动
func WatchConfig(c *config) error {
if err := LoadConfigFromYaml(c); err !=nil{
return err;
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background());
c.v.WatchConfig()
//监听回调函数
watch := func(e fsnotify.Event) {
log.Printf("Config file is changed: %s \n", e.String())
cancel();
}
c.v.OnConfigChange(watch);
<-ctx.Done();
return nil;
}
重点来了啊,这个可以说是非常非常实用的一个功能,以往我们修改配置文件要么重启服务,要么搞一个api去修改,Viper把这个功能帮我们实现了。只要配置文件被修改保存后,我们事先注册的watch函数就回被触发,只要我们在这里面添加更新操作就ok了。不过美中不足的是,它目前只监听配置文件。
拷贝子分支
func TestSubConfig(t *testing.T) {
c := config{};
LoadConfigFromYaml(&c);
sc := c.v.Sub("information");
sc.Set("age", 80);
scs,_:=yaml.Marshal(sc.AllSettings())
t.Log(string(scs));
t.Logf("age: %d", c.v.GetInt("information.age"));
}
拷贝一个子分支最大的用途就是我们可以复制一份配置,这样在修改拷贝的时候原配置不会被修改,如果修改的配置出现了问题,我们可以方便的回滚。
获取配置项的方法
//测试各种get类型
func TestGetValues(t *testing.T) {
c := &config{}
if err := LoadConfigFromYaml(c); err != nil{
t.Fatalf("%s: %s",t.Name(), err.Error());
}
if info := c.v.GetStringMap("information"); info != nil{
t.Logf("%T", info);
}
if aliases := c.v.GetStringSlice("information.aliases"); aliases != nil{
for _, a := range aliases{
t.Logf("%s",a);
}
}
timeStamp := c.v.GetTime("timestamp");
t.Logf("%s", timeStamp.String());
if public := c.v.GetBool("information.public"); public{
t.Logf("the information is public");
}
age := c.v.GetInt("information.age");
t.Logf("%s age is %d", c.v.GetString("information.name"), age);
}
如果我们直接用Get获取的返回值都是interface{}类型,这样我们还要手动转化一下,可以直接指定类型去获取,方便快捷。
除了以上所说的功能外,viper还有从etcd提取配置以及自定义flage的功能,这些大家感兴趣可以自己去了解一下。
有趣的应用
虽然Unmarshal Struct已经足够好用了,但有作者还是想开发一下新的玩法,比如说这个配置文件和当前的新版本不是很匹配,当然实际生产中我们是要讲究向下兼容的。
var yamlConfig = YamlConfig{};
ycType := reflect.TypeOf(yamlConfig);
for i := 0 ; i < ycType.NumField();i++{
name := ycType.Field(i).Name;
element := reflect.ValueOf(yamlConfig).Field(i).Interface();
if err = config.UnmarshalKey(name, element); err != nil{
logger.Errorf("Error reading configuration:", err);
}
}
如上代码所示,我们从最外围的结构体中找出子元素的名
还有一篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/sd653159/article/details/83143760
前言
viper 支持Yaml、Json、 TOML、HCL 等格式,读取非常的方便。
安装
go get github.com/spf13/viper
如果提示找不到golang.org/x/text/这个库,是因为golang.org/x/text/这个库在GitHub上托管的路径不一致。
解决办法:
可以从https://github.com/golang/text下载源码下来,然后到$GOPATH/src下面创建golang.org/x/文件夹(已存在的忽略),把压缩包的文件解压到golang.org/x/文件夹之下。
然后执行 go install -x golang.org/x/text 即可解决:
正文
初始结构目录如下:
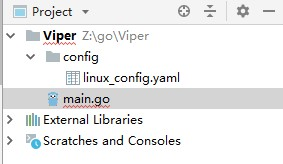
准备测试使用的yaml文件,注意yaml的格式十分严格,主要是每个冒号后面必须要有空格,数组前要加“-”号表示连续(注意减号后面也有空格),内容如下:
TimeStamp: "2018-10-18 10:09:23"
Address: "Shenzhen"
Postcode: 518000
CompanyInfomation:
Name: "Sunny"
MarketCapitalization: 50000000
EmployeeNum: 200
Department:
- "Finance"
- "Design"
- "Program"
- "Sales"
IsOpen: false
读取yaml文件:
package main
import (
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//读取yaml文件
v := viper.New()
//设置读取的配置文件
v.SetConfigName("linux_config")
//添加读取的配置文件路径
v.AddConfigPath("./config/")
//windows环境下为%GOPATH,linux环境下为$GOPATH
v.AddConfigPath("$GOPATH/src/")
//设置配置文件类型
v.SetConfigType("yaml")
if err := v.ReadInConfig();err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err:%s\n",err)
}
fmt.Printf(
`
TimeStamp:%s
CompanyInfomation.Name:%s
CompanyInfomation.Department:%s `,
v.Get("TimeStamp"),
v.Get("CompanyInfomation.Name"),
v.Get("CompanyInfomation.Department"),
)
/*
result:
TimeStamp:2018-10-18 10:09:23
CompanyInfomation.Name:Sunny
CompanyInfomation.Department:[Finance Design Program Sales]
*/
}
也可以直接反序列化为Struct,非常的方便:
package main
import (
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//读取yaml文件
v := viper.New()
//设置读取的配置文件
v.SetConfigName("linux_config")
//添加读取的配置文件路径
v.AddConfigPath("./config/")
//windows环境下为%GOPATH,linux环境下为$GOPATH
v.AddConfigPath("$GOPATH/src/")
//设置配置文件类型
v.SetConfigType("yaml")
if err := v.ReadInConfig();err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err:%s\n",err)
}
fmt.Printf(
`
TimeStamp:%s
CompanyInfomation.Name:%s
CompanyInfomation.Department:%s `,
v.Get("TimeStamp"),
v.Get("CompanyInfomation.Name"),
v.Get("CompanyInfomation.Department"),
)
/*
result:
TimeStamp:2018-10-18 10:09:23
CompanyInfomation.Name:Sunny
CompanyInfomation.Department:[Finance Design Program Sales]
*/
//反序列化
parseYaml(v)
}
type CompanyInfomation struct{
Name string
MarketCapitalization int64
EmployeeNum int64
Department []interface{}
IsOpen bool
}
type YamlSetting struct{
TimeStamp string
Address string
Postcode int64
CompanyInfomation CompanyInfomation
}
func parseYaml(v *viper.Viper){
var yamlObj YamlSetting;
if err := v.Unmarshal(&yamlObj) ; err != nil{
fmt.Printf("err:%s",err)
}
fmt.Println(yamlObj)
/*
result:
{2018-10-18 10:09:23 Shenzhen 518000 {Sunny 50000000 200 [Finance Design Program Sales] false}}
*/
}
viper也提供了读取Command Line参数的功能:
package main
import (
"github.com/spf13/pflag"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
pflag.String("hostAddress", "127.0.0.1", "Server running address")
pflag.Int64("port", 8080, "Server running port")
pflag.Parse()
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine)
fmt.Printf("hostAddress :%s , port:%s", viper.GetString("hostAddress"), viper.GetString("port"))
/*
example:
go run main2.go --hostAddress=192.192.1.10 --port=9000
help:
Usage of /tmp/go-build183981952/b001/exe/main:
--hostAddress string Server running address (default "127.0.0.1")
--port int Server running port (default 8080)
*/
}
很多时候,我们服务器启动之后,如果临时想修改某些配置参数,需要重启服务器才能生效,但是viper提供了监听函数,可以免重启修改配置参数,非常的实用:
package main
import (
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"fmt"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify"
)
func main() {
//读取yaml文件
v := viper.New()
//设置读取的配置文件
v.SetConfigName("linux_config")
//添加读取的配置文件路径
v.AddConfigPath("./config/")
//windows环境下为%GOPATH,linux环境下为$GOPATH
v.AddConfigPath("$GOPATH/src/")
//设置配置文件类型
v.SetConfigType("yaml")
if err := v.ReadInConfig(); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err:%s\n", err)
}
//创建一个信道等待关闭(模拟服务器环境)
ctx, _ := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
//cancel可以关闭信道
//ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
//设置监听回调函数
v.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
fmt.Printf("config is change :%s \n", e.String())
//cancel()
})
//开始监听
v.WatchConfig()
//信道不会主动关闭,可以主动调用cancel关闭
<-ctx.Done()
/*
result:
config is change :"/home/share/go/Viper/config/linux_config.yaml": CREATE
config is change :"/home/share/go/Viper/config/linux_config.yaml": CREATE
*/
}
文章出处:https://blog.csdn.net/sd653159/article/details/83143760
http://www.cnblogs.com/cnblogs-wangzhipeng/p/9484460.html