Openresty+Lua+Redis灰度发布
灰度发布,简单来说,就是根据各种条件,让一部分用户使用旧版本,另一部分用户使用新版本。百度百科中解释:灰度发布是指在黑与白之间,能够平滑过渡的一种发布方式。AB test就是一种灰度发布方式,让一部分用户继续用A,一部分用户开始用B,如果用户对B没有什么反对意见,那么逐步扩大范围,把所有用户都迁移到B上面 来。灰度发布可以保证整体系统的稳定,在初始灰度的时候就可以发现、调整问题,以保证其影响度。上述描述的灰度方案A和B需要等量的服务器,这里我们所做的灰度发布稍作改变:用1-2台机器作为B,B测试成功再部署A。用于WEB系统新代码的测试发布,让一部分(IP)用户访问新版本,一部分用户仍然访问正常版本,原理如图:
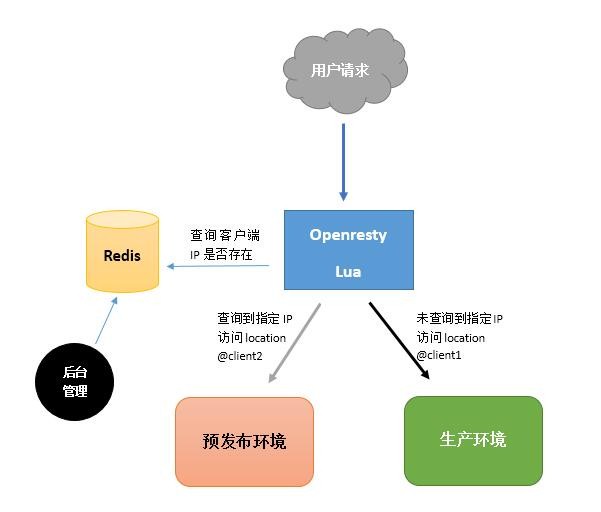
执行过程:
1、当用户请求到达前端web(代理)服务器Openresty,内嵌的lua模块解析Nginx配置文件中的lua脚本代码;
2、Lua获取客户端IP地址,去查询Redis中是否有该键值,如果有返回值执行@clien2,否则执行@client1。
3、Location @client2把请求转发给预发布服务器,location @client1把请求转发给生产服务器,服务器返回结果,整个过程完成。
Openresty部分配置如下:
upstream client1 { server 127.0.0.1:8080; #模拟生产服务器 } upstream client2 { server 127.0.0.1:8090; #模拟预发布服务器 } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location ^~ /test { content_by_lua_file /app/ngx_openresty/nginx/conf/huidu.lua } location @client1{ proxy_pass http://client1; } location @client2{ proxy_pass http://client2; } }
Lua脚本内容如下:
local redis = require "resty.redis" local cache = redis.new() cache:set_timeout(60000) local ok, err = cache.connect(cache, '127.0.0.1', 6379) if not ok then ngx.say("failed to connect:", err) return end local red, err = cache:auth("foobared") if not red then ngx.say("failed to authenticate: ", err) return end local local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"] if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"] end if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.var.remote_addr end --ngx.say("local_ip is : ", local_ip) local intercept = cache:get(local_ip) if intercept == local_ip then ngx.exec("@client2") return end ngx.exec("@client1") local ok, err = cache:close() if not ok then ngx.say("failed to close:", err) return end
验证:
url:http://192.168.116.145/test/n.jpg (模拟生产环境)
客户端IP:192.168.116.1(模拟公司办公网IP)
1、访问http://192.168.116.145/test/n.jpg
返回的结果是生产服务器的。

在Redis存入客户端IP:
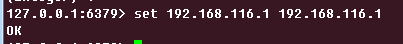
继续访问:
请求到的是预发布服务器返回的结果。

在Redis中删除客户端IP:
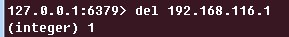
然后刷新浏览器:
返回生产服务器的结果。
灰度发布,简单来说,就是根据各种条件,让一部分用户使用旧版本,另一部分用户使用新版本。百度百科中解释:灰度发布是指在黑与白之间,能够平滑过渡的一种发布方式。AB test就是一种灰度发布方式,让一部分用户继续用A,一部分用户开始用B,如果用户对B没有什么反对意见,那么逐步扩大范围,把所有用户都迁移到B上面 来。灰度发布可以保证整体系统的稳定,在初始灰度的时候就可以发现、调整问题,以保证其影响度。上述描述的灰度方案A和B需要等量的服务器,这里我们所做的灰度发布稍作改变:用1-2台机器作为B,B测试成功再部署A。用于WEB系统新代码的测试发布,让一部分(IP)用户访问新版本,一部分用户仍然访问正常版本,原理如图:

执行过程:
1、当用户请求到达前端web(代理)服务器Openresty,内嵌的lua模块解析Nginx配置文件中的lua脚本代码;
2、Lua获取客户端IP地址,去查询Redis中是否有该键值,如果有返回值执行@clien2,否则执行@client1。
3、Location @client2把请求转发给预发布服务器,location @client1把请求转发给生产服务器,服务器返回结果,整个过程完成。
Openresty部分配置如下:
upstream client1 { server 127.0.0.1:8080; #模拟生产服务器 } upstream client2 { server 127.0.0.1:8090; #模拟预发布服务器 } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location ^~ /test { content_by_lua_file /app/ngx_openresty/nginx/conf/huidu.lua } location @client1{ proxy_pass http://client1; } location @client2{ proxy_pass http://client2; } }
Lua脚本内容如下:
local redis = require "resty.redis" local cache = redis.new() cache:set_timeout(60000) local ok, err = cache.connect(cache, '127.0.0.1', 6379) if not ok then ngx.say("failed to connect:", err) return end local red, err = cache:auth("foobared") if not red then ngx.say("failed to authenticate: ", err) return end local local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"] if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"] end if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.var.remote_addr end --ngx.say("local_ip is : ", local_ip) local intercept = cache:get(local_ip) if intercept == local_ip then ngx.exec("@client2") return end ngx.exec("@client1") local ok, err = cache:close() if not ok then ngx.say("failed to close:", err) return end
验证:
url:http://192.168.116.145/test/n.jpg (模拟生产环境)
客户端IP:192.168.116.1(模拟公司办公网IP)
1、访问http://192.168.116.145/test/n.jpg
返回的结果是生产服务器的。

在Redis存入客户端IP:

继续访问:
请求到的是预发布服务器返回的结果。

在Redis中删除客户端IP:

然后刷新浏览器:
返回生产服务器的结果。
