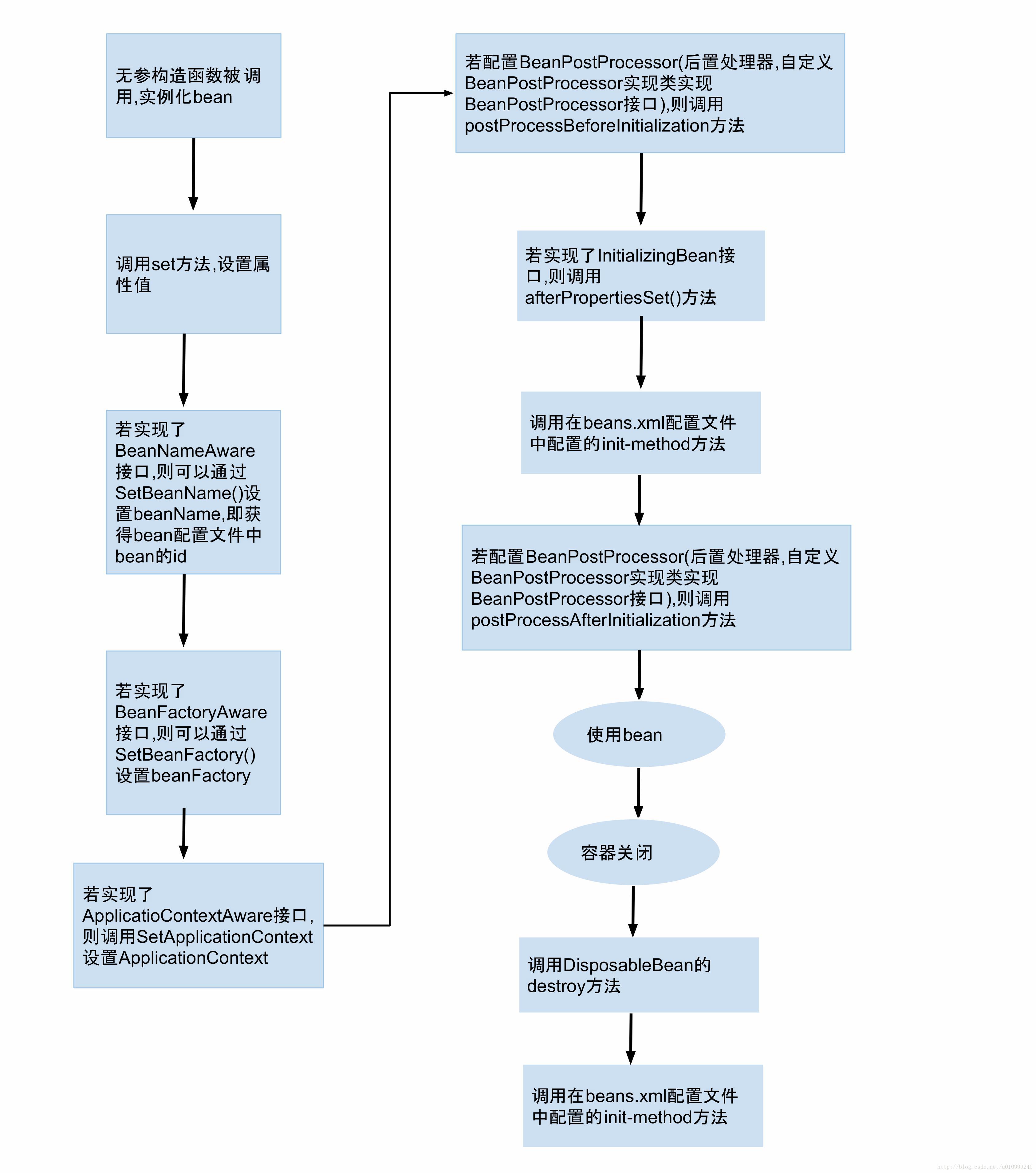
spring中bean的生命周期详解
首先,beans.xml文件配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="personService" class="com.beanlife.PersonService" init-method="init" destroy-method="destoryBean">
<property name="name" >
<value>siege</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.beanlife.MyBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
</beans>PersonService.java
package com.beanlife;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class PersonService implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
public PersonService() {
super();
System.out.println("PersonService被创建");
}
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("setName被调用");
}
public void showName(){
System.out.println(this.name);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext appliactionContext)throws BeansException {
System.out.println(appliactionContext);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用afterPropertiesSet()方法");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("init方法被调用");
}
public void destoryBean(){
System.out.println("destoryBean方法被调用");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
继承BeanPostProcessor实现后置处理器的MyBeanPostProcessor.java
package com.beanlife;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)throws BeansException {
System.out.println("*********postProcessAfterInitialization**************");
System.out.println(arg0);
System.out.println(arg1);
System.out.println("*********postProcessAfterInitialization**************");
return arg0;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)throws BeansException {
System.out.println("*********postProcessBeforeInitialization**************");
System.out.println(arg0);
System.out.println(arg1);
System.out.println("*********postProcessBeforeInitialization**************");
return arg0;
}
}
测试类Test.java
package com.beanlife;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/beanlife/beans.xml");
PersonService p=(PersonService) ac.getBean("personService");
p.showName();
}
}测试结果如下:
PersonService被创建
setName被调用
personService
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@a068d1: defining beans [personService,myBeanPostProcessor]; root of factory hierarchy
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@75222b: display name [org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@75222b]; startup date [Sat Jan 31 21:36:08 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchy
*********postProcessBeforeInitialization**************
com.beanlife.PersonService@4f701
personService
*********postProcessBeforeInitialization**************
调用afterPropertiesSet()方法
init方法被调用
*********postProcessAfterInitialization**************
com.beanlife.PersonService@4f701
personService
*********postProcessAfterInitialization**************
siege 若通过beanFactory获取bean,即修改Test.java文件为:
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("com/beanlife/beans.xml"));
PersonService p=(PersonService) factory.getBean("personService");
则测试结果为:
PersonService被创建
setName被调用
personService
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory@11274d2: defining beans [personService,myBeanPostProcessor]; root of factory hierarchy
调用afterPropertiesSet()方法
init方法被调用
siege 整个bean的生命周期如下图: